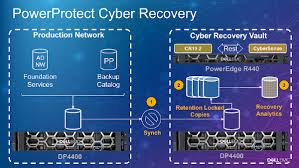
What Is Cyber Recovery, In today’s digital age, the threat landscape is constantly evolving, and organizations face increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks. Protecting data and critical systems from breaches is paramount, but what happens when preventive measures fail? This is where cyber recovery comes into play. Cyber recovery is a structured strategy designed to restore business operations and recover compromised data following a cyberattack, minimizing downtime and safeguarding valuable information.
What is Cyber Recovery?
Cyber recovery refers to the process and set of technologies used to restore systems and data after a cyber incident, such as ransomware attacks, data breaches, or malware infiltration. While traditional data backup and disaster recovery solutions focus on recovering from hardware failures or natural disasters, cyber recovery specifically addresses recovery from cyber threats.
The goal of cyber recovery is not only to bring systems back online but also to ensure that the restored data is free of malware or any malicious modifications. This is achieved by creating secure, isolated backup environments that are protected from attack and regularly tested for integrity.
Key Components of Cyber Recovery
- Isolated Backup Vaults: Unlike regular backups that may be susceptible to attacks, a cyber recovery solution typically uses a highly secured and isolated vault where copies of critical data are stored. This vault is disconnected from the main network to ensure it is out of reach for cybercriminals.
- Immutable Data Storage: Data stored in a cyber recovery vault is often immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted by unauthorized users. This prevents attackers from encrypting or corrupting backup files during a cyber incident.
- Regular Backup and Testing: Cyber recovery solutions require frequent backups and rigorous testing. The integrity of the stored data is checked continuously to ensure it is free from malware or other corruption. Testing recovery procedures also ensures a swift and smooth restoration process in the event of an attack.
- Incident Response and Recovery Plans: A critical part of cyber recovery is having a well-documented and rehearsed response plan. This includes identifying the extent of the damage, containing the incident, and initiating the recovery process as quickly as possible.
- Advanced Analytics and Forensics: Many cyber recovery solutions are equipped with advanced analytics tools that allow organizations to detect any abnormal activities in backup data. These tools help in identifying whether the backups themselves are compromised and ensure that only clean data is restored.
Why is Cyber Recovery Important?
- Rising Cyber Threats: The increase in ransomware and other forms of cyberattacks has made traditional recovery methods insufficient. Attackers are getting more skilled at infiltrating backup systems and sabotaging recovery efforts. Cyber recovery adds an extra layer of security to ensure that even if an attack is successful, recovery is still possible.
- Business Continuity: Cyberattacks can lead to significant downtime, and for many organizations, downtime equals financial loss. Cyber recovery minimizes downtime, ensuring businesses can resume operations as quickly as possible after an attack.
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Many industries are subject to regulations that require them to have robust recovery mechanisms in place. Cyber recovery solutions can help organizations meet these requirements, avoiding potential fines and legal consequences.
- Maintaining Reputation: Recovering from a cyberattack can be damaging not only financially but also in terms of reputation. A slow or ineffective recovery can lead to loss of customer trust. A strong cyber recovery plan ensures organizations can recover quickly and maintain their reputation.
Cyber Recovery vs. Disaster Recovery
While both cyber recovery and disaster recovery are essential to an organization’s overall resilience, they address different types of threats. Disaster recovery typically focuses on restoring data and operations following physical disasters like floods, fires, or power outages. Cyber recovery, on the other hand, specifically targets restoring systems after cyberattacks.
A key difference lies in the level of protection required. In disaster recovery, the main concern is recovering lost data, whereas in cyber recovery, there is an added focus on ensuring that the recovered data is clean and free from malicious code.
Best Practices for Cyber Recovery
- Segregate Backups: Ensure that backup environments are isolated from the main network to prevent attackers from accessing them.
- Use Encryption: All backups should be encrypted both in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Protect access to backup systems with MFA to ensure that only authorized users can make changes.
- Regularly Update Security Protocols: Cyber threats evolve constantly, so it is essential to keep security measures up to date.
- Conduct Regular Drills: Testing cyber recovery plans through regular drills helps identify potential gaps and improves readiness.
Conclusion
Cyber recovery is a vital part of modern cybersecurity strategies. As cyberattacks grow in frequency and complexity, organizations must go beyond traditional recovery methods and implement dedicated cyber recovery solutions to protect their most valuable assets. By isolating backups, ensuring data integrity, and having well-tested response plans, companies can significantly reduce the risks and impact of a cyber incident.
You Might Also Like These:
Cyber-Physical System Checkpointing and Recovery: Ensuring Resilience in Modern Systems
The Importance of Disaster Recovery in Cybersecurity
Mimecast: How Many Days of Data Recovery in Cyber Resilience?
Mimecast: 180 Days of Data Recovery and Cyber Resilience
Cyber Defense Disaster Recovery Conference: Preparing for the Future of Cybersecurity