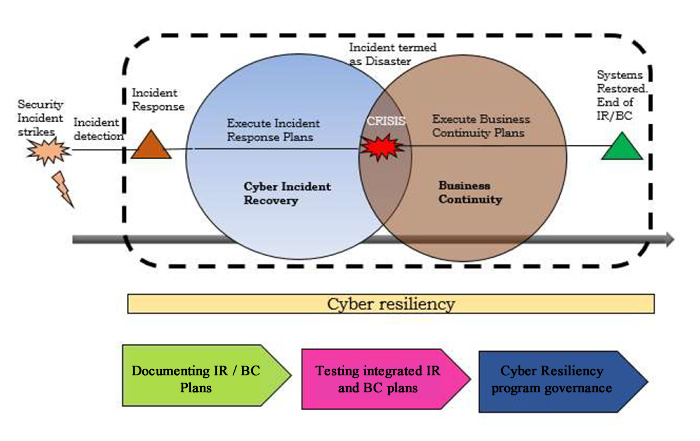
Business Continuity And Disaster Recovery In Cyber Security, In today’s digital landscape, the significance of cybersecurity has never been greater. With businesses increasingly reliant on technology and data, the threats posed by cyberattacks are evolving and intensifying. As a result, organizations must not only implement robust security measures but also prepare for potential disruptions through effective business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) strategies. This article explores the essential elements of BCDR in the context of cybersecurity, highlighting their importance, components, and best practices.
Understanding Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Business Continuity (BC)
Business continuity refers to the processes and plans that organizations implement to ensure that critical business functions can continue during and after a disruptive event. This could range from natural disasters to cyber incidents such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, or system failures. The primary goal of business continuity is to minimize downtime and maintain operations, ensuring that the organization can serve its clients and stakeholders without significant interruption.
Disaster Recovery (DR)
Disaster recovery, on the other hand, focuses specifically on the recovery of IT infrastructure and operations after a disaster. This includes restoring data, applications, and hardware that may have been compromised or lost due to an incident. While disaster recovery is a subset of business continuity, it is crucial for ensuring that an organization can resume normal operations and protect its digital assets.
The Importance of BCDR in Cybersecurity
- Risk Mitigation: Cyber threats can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences. A well-defined BCDR strategy helps organizations identify potential risks and implement measures to mitigate them effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations that mandate certain standards for data protection and incident response. A comprehensive BCDR plan ensures compliance with these regulations, helping organizations avoid costly penalties.
- Reassurance for Stakeholders: Clients, partners, and investors are increasingly concerned about cybersecurity risks. Demonstrating a commitment to business continuity and disaster recovery can enhance trust and confidence among stakeholders.
- Quick Recovery: In the event of a cyber incident, time is of the essence. A solid BCDR plan enables organizations to respond quickly, minimizing downtime and potential losses.
Key Components of an Effective BCDR Strategy
- Risk Assessment: Conducting a thorough risk assessment is the first step in developing a BCDR strategy. Organizations should identify critical assets, potential threats, and vulnerabilities to determine the necessary measures for protection.
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA): A BIA helps organizations understand the potential impact of disruptions on their operations. This analysis prioritizes business functions and resources, guiding the development of recovery strategies.
- Plan Development: The BCDR plan should outline specific procedures for responding to incidents, including roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and recovery steps. This plan should be detailed, accessible, and regularly updated.
- Testing and Training: Regular testing of BCDR plans is essential to ensure their effectiveness. Organizations should conduct drills and simulations to prepare staff for potential incidents. Training employees on their roles within the BCDR framework fosters a culture of preparedness.
- Continuous Improvement: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and so should BCDR strategies. Organizations must regularly review and update their plans based on new threats, lessons learned from past incidents, and changes in business operations.
Best Practices for Implementing BCDR in Cybersecurity
- Leverage Technology: Utilize advanced technologies such as cloud computing, data backup solutions, and cybersecurity tools to enhance resilience and recovery capabilities.
- Establish Clear Communication: Ensure that communication channels are defined and tested. Stakeholders should know who to contact and how information will be disseminated during a crisis.
- Involve Leadership: Engage senior management and key stakeholders in the development and review of BCDR plans. Their support is crucial for resource allocation and fostering a culture of security.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of emerging cyber threats and trends. Regularly updating the BCDR strategy to reflect the evolving threat landscape is critical for maintaining effectiveness.
- Document Everything: Maintain detailed records of all BCDR-related activities, including risk assessments, training sessions, and plan revisions. Documentation helps with compliance and serves as a reference for future improvements.
Conclusion
In an era where cyber threats are pervasive and constantly evolving, business continuity and disaster recovery are essential components of a robust cybersecurity strategy. By understanding the importance of BCDR, organizations can mitigate risks, ensure compliance, and maintain operational resilience. Implementing a comprehensive BCDR plan not only protects digital assets but also enhances stakeholder confidence and prepares businesses to thrive in the face of adversity.
You Might Also Like These: