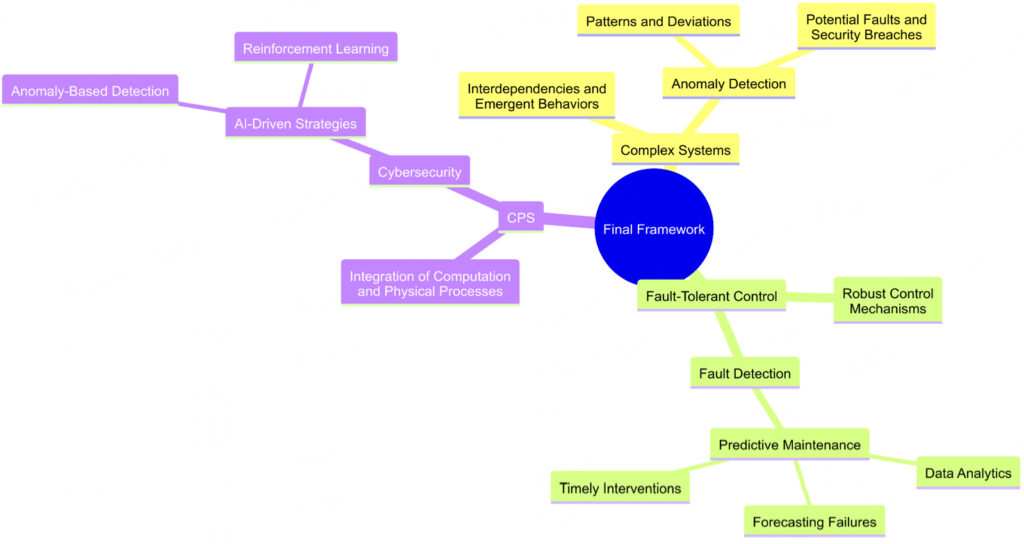
Cyber Fault-Tolerant Attack Recovery (Cfar), In today’s interconnected world, organizations face an ever-increasing number of cyber threats that can disrupt operations and compromise sensitive data. To counter these risks, the concept of Cyber Fault-Tolerant Attack Recovery (CFAR) has emerged as a critical framework for enhancing resilience against cyber attacks. CFAR focuses on maintaining operational continuity and minimizing downtime, enabling organizations to recover quickly and effectively from cyber incidents.
Understanding CFAR
CFAR refers to a systematic approach that integrates fault tolerance and recovery strategies into an organization’s cybersecurity infrastructure. It emphasizes the importance of not just preventing attacks but also preparing for effective recovery in the event of a breach or failure. This dual focus on prevention and recovery is crucial, as it allows organizations to respond to threats while ensuring that critical systems remain operational.
Key components of CFAR include:
- Redundancy: Implementing redundant systems and networks ensures that if one component fails due to an attack, others can take over, allowing for seamless operations. This can involve duplicating data across different servers or utilizing cloud-based solutions for backup.
- Real-time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of network traffic and system performance helps identify anomalies that may indicate a cyber attack. By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning, organizations can detect and respond to threats in real time, reducing the impact of any breach.
- Automated Response Mechanisms: CFAR emphasizes the use of automation in recovery processes. Automated systems can quickly isolate affected components, reroute traffic, and restore services without requiring manual intervention, thus minimizing downtime.
- Incident Response Planning: A well-defined incident response plan is essential for effective recovery. This plan should outline roles and responsibilities, communication strategies, and recovery procedures to ensure that all stakeholders are prepared to act swiftly during an incident.
- Regular Testing and Updates: Regularly testing recovery plans and updating systems are crucial to ensure that organizations can adapt to new threats and vulnerabilities. Simulation exercises can help teams practice their response strategies and identify areas for improvement.
Benefits of CFAR
The implementation of CFAR offers several benefits to organizations, including:
- Enhanced Resilience: By adopting a proactive approach to attack recovery, organizations can reduce the risk of extended downtime and maintain service continuity.
- Improved Trust and Reputation: Clients and customers are more likely to trust organizations that demonstrate a commitment to cybersecurity and have robust recovery strategies in place.
- Cost Savings: Reducing downtime and improving recovery times can lead to significant cost savings, especially for businesses that rely heavily on digital operations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements regarding data protection and incident response. CFAR can help organizations meet these compliance standards, reducing legal and financial risks.
Conclusion
In an era where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated and prevalent, Cyber Fault-Tolerant Attack Recovery (CFAR) is an essential strategy for organizations seeking to safeguard their operations. By focusing on resilience, redundancy, and recovery planning, organizations can better prepare for cyber incidents and minimize their impact. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, investing in CFAR will be crucial for maintaining operational integrity and ensuring long-term success in the face of cyber challenges.
You Might Also Like These: