Incident Recovery In Cyber Security, In the digital age, where cyber threats are an ever-present reality, the importance of robust incident recovery in cyber security cannot be overstated. Organizations of all sizes face potential attacks, ranging from data breaches and ransomware to denial-of-service attacks. An effective incident recovery plan is crucial for minimizing damage and ensuring business continuity. This article explores the key components of incident recovery in cyber security and offers practical strategies for organizations to enhance their recovery efforts.
Understanding Incident Recovery
Incident recovery refers to the process of restoring systems, data, and operations after a cyber security incident. This phase is critical for organizations as it involves assessing the damage, containing the threat, and recovering affected systems to ensure that business operations can continue with minimal disruption.
The Importance of Incident Recovery Planning
A well-defined incident recovery plan (IRP) is vital for several reasons:
- Minimizing Downtime: Quick recovery from incidents reduces the impact on business operations and customer trust.
- Protecting Data Integrity: Ensuring that data is restored accurately helps maintain the integrity of business processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have legal and regulatory requirements for incident recovery that must be met to avoid penalties.
- Reputation Management: Effective recovery can mitigate reputational damage that often accompanies cyber incidents.
Key Components of an Incident Recovery Plan
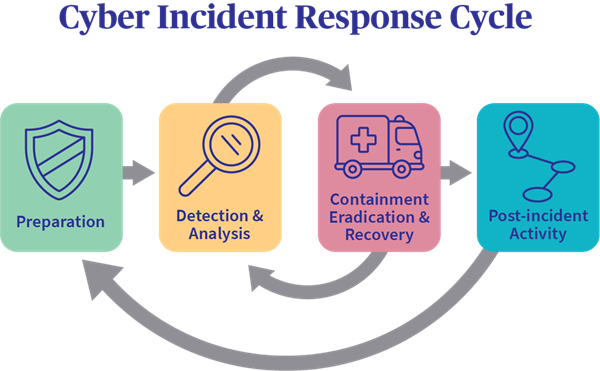
1. Preparation
Preparation involves creating and documenting an incident recovery strategy. This includes:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities specific to the organization.
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring that necessary resources (both human and technological) are in place.
- Training and Awareness: Conducting regular training for employees to recognize potential threats and understand their roles in recovery.
2. Detection and Analysis
Once an incident occurs, swift detection and analysis are critical. This involves:
- Monitoring Tools: Implementing security information and event management (SIEM) systems to detect anomalies.
- Incident Classification: Categorizing incidents based on severity to prioritize response efforts.
3. Containment
Containment is crucial to prevent the incident from escalating. Strategies include:
- Isolation: Disconnecting affected systems from the network to limit further damage.
- Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed about the incident and the steps being taken.
4. Eradication
After containment, organizations must eliminate the threat. This involves:
- Root Cause Analysis: Identifying the source of the incident to prevent recurrence.
- System Clean-Up: Removing malicious software and repairing vulnerabilities.
5. Recovery
The recovery phase focuses on restoring systems and data. Key steps include:
- Data Restoration: Recovering data from backups to restore normal operations.
- System Testing: Ensuring that systems are fully functional and secure before going live.
6. Post-Incident Review
A thorough review following an incident is essential for continuous improvement. This includes:
- Documentation: Recording details of the incident, response actions, and recovery efforts.
- Lessons Learned: Analyzing what worked well and what didn’t to improve future incident recovery processes.
Best Practices for Incident Recovery
- Regularly Update the Incident Recovery Plan: Ensure that the IRP is current and reflects any changes in the organizational structure or threat landscape.
- Conduct Drills and Simulations: Regularly test the incident recovery plan through drills to identify weaknesses and improve response time.
- Leverage Automation: Utilize automated recovery tools to speed up the recovery process and reduce human error.
- Engage Third-Party Experts: In complex incidents, having cybersecurity consultants can provide valuable insights and resources.
Conclusion
Incident recovery in cyber security is an ongoing process that requires careful planning, execution, and refinement. By understanding the components of an effective incident recovery plan and implementing best practices, organizations can enhance their resilience against cyber threats. In a world where cyber incidents are inevitable, being prepared can make all the difference in maintaining operational continuity and protecting sensitive data.
You Might Also Like These: